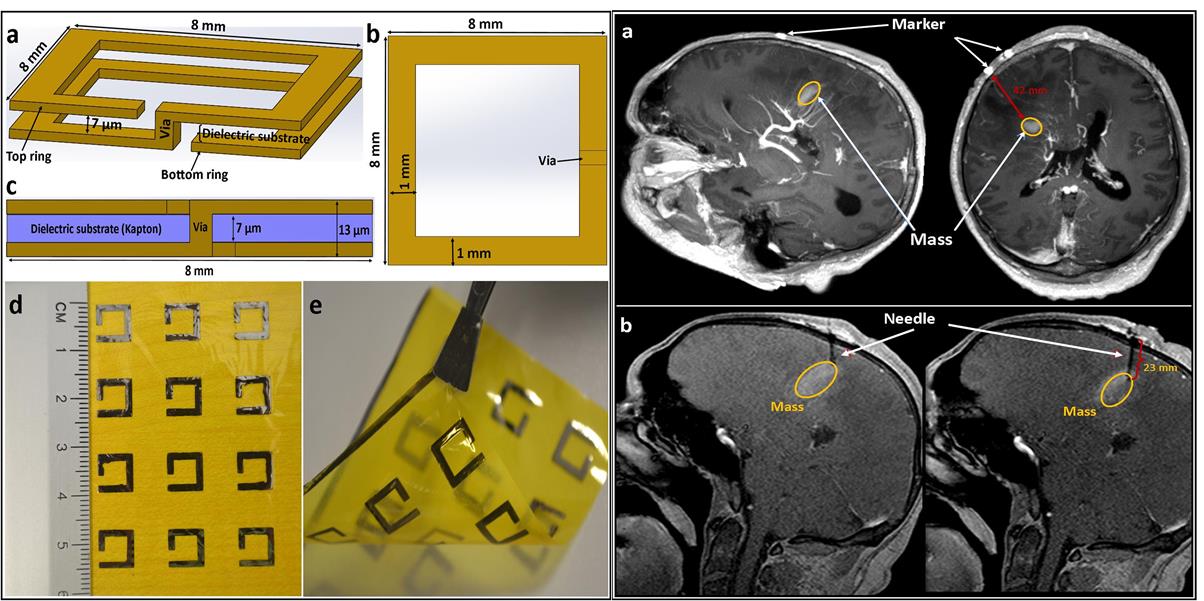
UMRAM researchers published a novel work in MRM journal in collaborating with UNAM team. This study presents an inductively coupled ultra-thin, flexible, and passive RF resonator for MRI marking and guiding purposes with clinical feasibility. Standard microfabrication processing was used to fabricate the resonant marker.
The proposed marker consists of two metal traces in the shape of a square with an edge length of 8 mm, with upper and lower traces connected to each other by a metalized via. A 3T MRI fiducial marking procedure was tested in phantom and ex vivo, and then the marker’s performance was evaluated in an MRI experiment using humans. The ultra-thin and flexible structure of this wireless flexible RF resonant marker offers effective and safe MR visualization with high feasibility for anatomic marking and guiding in various regions of the body.